Comparison of Corsort variants
This notebook shows how to use the corsort package to compare different variants of Corsorts. In details we tested the following possibilities:
Internal scorer: \(\Delta\) or \(\rho\)
Information measure: \(I(i)+I(j)\) or \(\max(I(i), I(j))\)
External scorer: \(\Delta\) or \(\rho\)
There are much more variants available. We restrain to these 8 for conciseness.
First we load some packages.
[1]:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from multiprocess.pool import Pool
from corsort import *
We populate the list of corsorts we want to study.
[2]:
sort_list = [
JitCorsortDeltaSumDelta(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortDeltaMaxDelta(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortRhoSumDelta(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortRhoMaxDelta(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortRhoSumRho(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortRhoMaxRho(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortDeltaSumRho(compute_history=True),
JitCorsortDeltaMaxRho(compute_history=True)]
legends = {'corsort_delta_sum_delta': r'Corsort-$\Delta\sum$ $\Delta$',
'corsort_delta_max_delta': r'Corsort-$\Delta$Max $\Delta$',
'corsort_rho_sum_delta': r'Corsort-$\rho\sum$ $\Delta$',
'corsort_rho_max_delta': r'Corsort-$\rho$Max $\Delta$',
'corsort_rho_sum_rho': r'Corsort-$\rho\sum$ $\rho$',
'corsort_rho_max_rho': r'Corsort-$\rho$Max $\rho$',
'corsort_delta_sum_rho': r'Corsort-$\Delta\sum$ $\rho$',
'corsort_delta_max_rho': r'Corsort-$\Delta$Max $\rho$'}
We decide the value of \(n\) to study and the number of trials.
[3]:
n = 500
nt = 10000
We now run the experiments, with some multi-processing to speed-up things.
[4]:
with Pool() as p:
convergence = evaluate_convergence(sort_list=sort_list, n=n, nt=nt, pool=p)
Evaluate convergence of corsort_delta_sum_delta for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [28:06<00:00, 5.93it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_delta_max_delta for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [27:59<00:00, 5.96it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_rho_sum_delta for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [30:50<00:00, 5.40it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_rho_max_delta for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [30:01<00:00, 5.55it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_rho_sum_rho for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [31:49<00:00, 5.24it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_rho_max_rho for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [30:45<00:00, 5.42it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_delta_sum_rho for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [28:10<00:00, 5.91it/s]
Evaluate convergence of corsort_delta_max_rho for n = 500
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [27:48<00:00, 5.99it/s]
We save the raw results.
[5]:
import dill as pickle
from pathlib import Path
fn = Path(f"corsorts_n_{n}_nt_{nt}.pkl")
if fn.exists():
with open(fn, 'rb') as f:
convergence = pickle.load(f)
else:
with open(fn, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(convergence, f)
Then we display the results.
[6]:
m = n*(n-1)/2
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
ax = plt.axes()
decim=40
color_dict = auto_colors(sort_list)
for name in legends:
ref = convergence[name]
color = color_dict[name]
p_m = ref.shape[1]
x = np.arange(p_m)[::decim]
ref = ref[:, ::decim]
q = np.zeros((5, ref.shape[1]))
for i, per in enumerate([2.5, 50, 97.5]):
q[i, :] = np.percentile(ref, per, axis=0)
q = q/m
ax.plot(x, q[1, :], label=legends[name], color=color)
ax.fill_between(x, q[0, :], q[2, :], alpha=.2, color=color)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
ax.tick_params(labelright=True, right=True)
plt.ylabel('Distance to sorted list')
plt.xlabel('Comparisons performed')
plt.ylim([0, None])
plt.xlim([0, None])
plt.show()
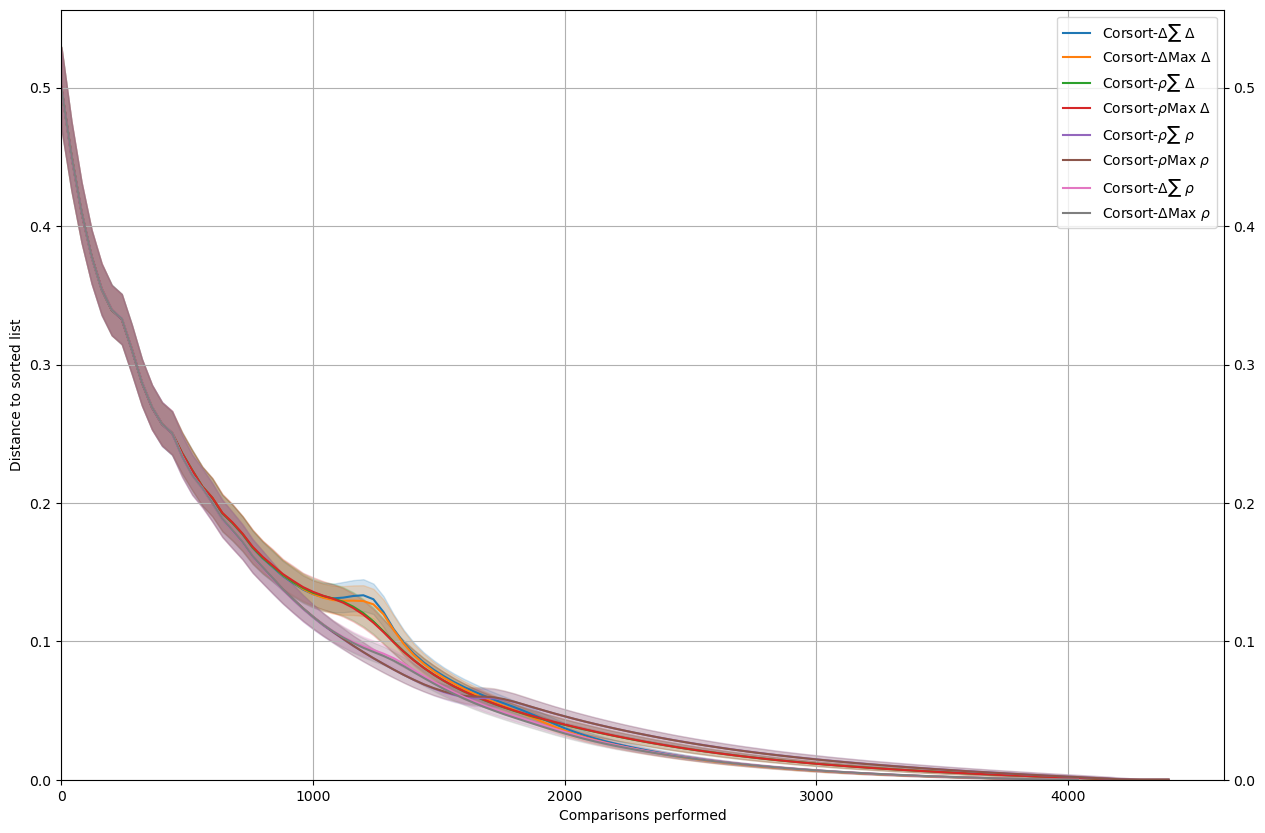
Quick interpretation :
maxandplusvariants (for measure of information) are very close to each other, with a slight advantage tomax.Using a \(\Delta\) external scorer creates a kind of bump. The \(\rho\) external scorer does not have this issue.
Most of the time (the exception been around the
bumpfrom previous item), the \(\Delta\) internal scorer is better.
In the end, we selected Corsort-\(\Delta\)Max \(\rho\):
Internal scorer: \(\Delta\)
Information measure: \(\max(I(i), I(j))\)
External scorer: \(\rho\)